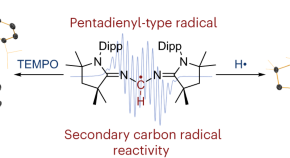
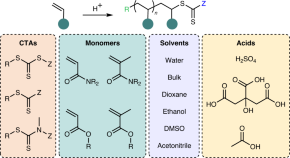
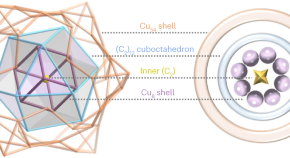
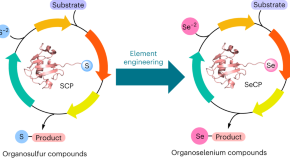
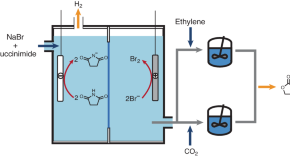
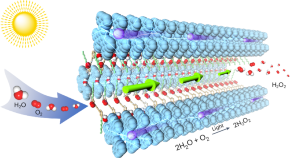
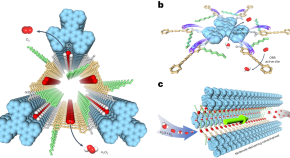
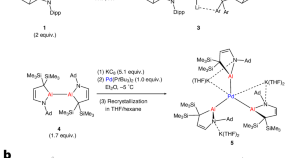
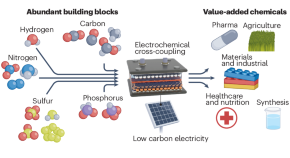
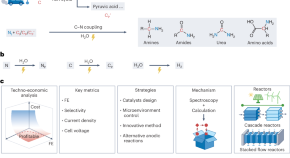
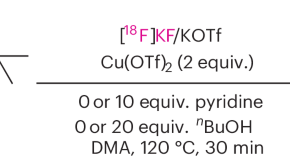
Featured

Advertisement
-
-

A radical development for enzymatic fluorination
Enzymes catalyse radical-mediated fluorine atom transfer reactions for enantioselective C(sp3)-F bond formation.
-
-